The File Browser provides direct access to files and folders on your hard drive. You can create new files and folders, search for files, open files in PrimalScript, and easily navigate between frequently used locations. You can even view and manage the security state of your files.
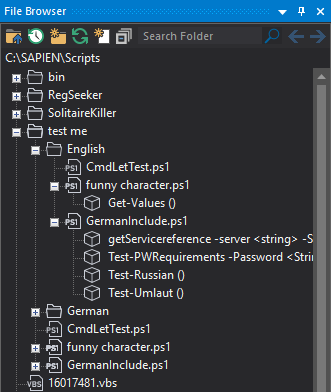
Accessing the File Browser
To show / hide the File Browser
•On the ribbon, click the View tab and then check (to show) or uncheck (to hide):
OR-
•Execute the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Alt + F.
File Browser - Buttons and Search
There are eight buttons, a search box, and a location field at the top of the File Browser:
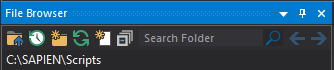
From left to right:
• Select Folder
Select Folder
Select a different folder in your environment as the current folder.
• Previous Folder
Previous Folder
Select a previously used folder as the current folder.
• New Folder
New Folder
Create a new empty folder in the current directory.
• Reload
Reload
Refresh the current folder.
• New File
New File
Create a new file.
 If the new file name has a known extension, the associated template is automatically applied.
If the new file name has a known extension, the associated template is automatically applied.
• Collapse Nodes
Collapse Nodes
Collapse all expanded nodes.
• Search Folder
Search Folder
Scans the current directory and displays all of the matching results.
• Previous Item
Previous Item
Go to the previous item matched by the current search.
• Next Item
Next Item
Go to the next item matched by the current search.
•Location
Displays the current directory.
File Browser - Context Menu Options
The context menu options will vary depending on what is selected in the File Browser (a folder, a file, a function, etc.) If a file is selected, the options will depend on the file type.
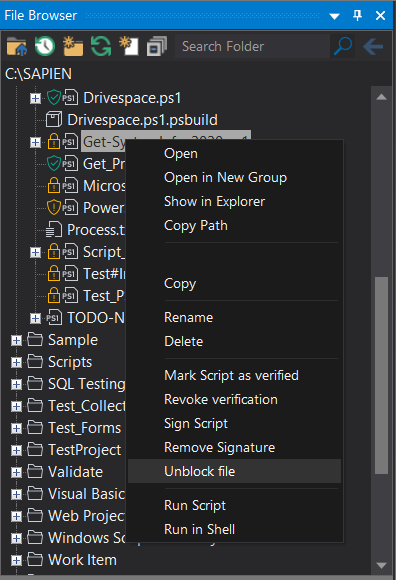
Right-click on a folder or file to display the following options:
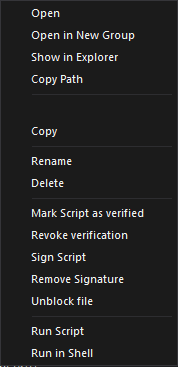
•Open
Opens the file in the Editor.
•Open in New Group
Opens the file in a new Editor group.
•Show in Explorer
Opens the corresponding file or folder location in File Explorer.
•Copy Path
Copies the full file or folder path to the clipboard.
•Copy
Copies the highlighted file to the clipboard.
•Rename
Highlights the file or folder name for editing.
•Delete
Deletes the highlighted file or folder.
•Mark Script as Verified, Revoke Verification, Sign Script, Remove Signature, Unblock File
See Security State of Scripts and Files.
•Run Script
Runs the script without loading it in the editor.
•Run in Shell
Runs the script in the Windows shell.
Right-click on a function to display the following options:
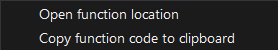
•Open function location
Opens the file in PrimalScript at the function's location.
•Copy function code to clipboard
Copies the function code from the file to the clipboard.
 You can also drag and drop the function code directly to your open script.
You can also drag and drop the function code directly to your open script.
Security State of Scripts and Files
The File Browser in PrimalScript and the SAPIEN Script Explorer both indicate the state of your scripts and other files by displaying a color-coded icon before the file name:
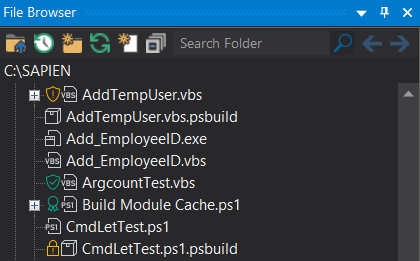
Security Icons:
• Blocked
Blocked
Recently downloaded from the internet or other source.
Windows applies an extended attribute to mark the file as "blocked".
• Signed
Signed
Signed with a certificate trusted by your computer. If there is a time stamp, it has a date and time before the certificate expires. The stored checksum of the file matches the current file.
• Verified
Verified
Marked as verified.
• Modified
Modified
Modified after being signed or verified.
•Blank (no icon)
The file does not have an extended attribute. The file does not have a valid signature, has not been verified, and has not been blocked.
 These color-coded security icons are also included in SAPIEN's Script Explorer, which is also a free download from your SAPIEN Account page.
These color-coded security icons are also included in SAPIEN's Script Explorer, which is also a free download from your SAPIEN Account page.
About Script Verification
Script verification creates a checksum over your script and stores it in an extended attribute. If someone else modifies the script, the checksum no longer matches.
Script verification has three states:
•Not Verified
The file does not have an extended attribute.
•Verified
You have marked the file as Verified.
•Modified
A file marked as Verified has subsequently been modified.
Files that have been marked as "verified" essentially have the same checksum feature of a digital signature, without the actual signature. Therefore, although script verification does not have the trusted standard of a digital certificate, it is the next best.
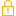
Using the File Browser
The File Browser has node indicators in front of some files that designate the file type. PrimalScript will also parse the files in your selected folder in the background and list any contained classes, methods, or functions:
 This applies to all file types PrimalScript knows, not just PowerShell files.
This applies to all file types PrimalScript knows, not just PowerShell files.
To open a file
•Double-click a file in the File Browser to open it in PrimalScript.
-OR-
•Drag a file from the File Browser and release it anywhere on the PrimalScript document or ribbon area.
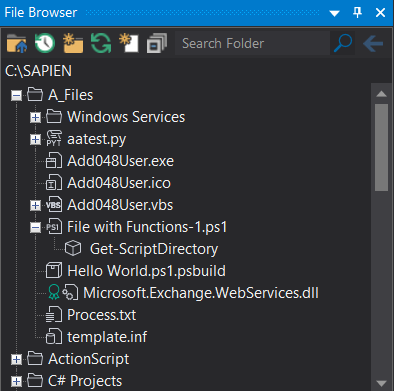
To open a file at the function's location
•Right-click a function in a file and select Open function location
-OR-
•Double-click a function in a file.
To copy the function
•Right-click and select Copy function code to clipboard
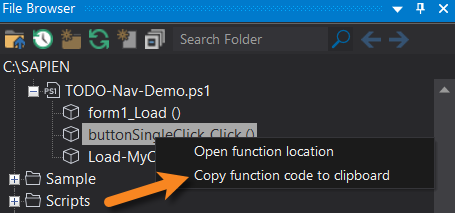
The function is copied from the file into the Windows clipboard.
 You can also drag the function code from the File Browser and drop it into your open file in the PrimalScript Editor.
You can also drag the function code from the File Browser and drop it into your open file in the PrimalScript Editor.
 PrimalScript will not interfere if you drag and drop between languages.
PrimalScript will not interfere if you drag and drop between languages.
To copy the full path name
•Hold the Shift key, then drag and drop a file from the File Browser into your open script to drop the full file path.
 If you drop a PowerShell file into your script it is enclosed in quotes and dot-sourced.
If you drop a PowerShell file into your script it is enclosed in quotes and dot-sourced.
To run a script
You can run scripts directly from the File browser without having to load them in the editor first.
•Right-click and select Run Script
 You can also run a script in the Windows shell.
You can also run a script in the Windows shell.
To unblock a file
•Right-click and select Unblock file
 Unblocking a file removes the extended attribute Windows added to the file when it was downloaded from a public or unsecure location or when it was extracted from a zip file with the same extended attribute.
Unblocking a file removes the extended attribute Windows added to the file when it was downloaded from a public or unsecure location or when it was extracted from a zip file with the same extended attribute.
See also: