A Windows Script Component (.wsc filename extension) is a special, XML-formatted file that allows a script to function as a COM object much like a DLL. Using the WSC format, you can essentially write your own modular COM components using VBScript or JScript. Although the XML format is complex, you don't need to worry about it because PrimalScript handles it all behind the scenes, allowing you to focus on your scripts.
In this topic we show you how to create, configure, and use a WSC project.
Starting a WSC
A WSC is a special kind of PrimalScript project. To begin one, select New Project, from the File menu. Under Windows Script Host Projects, select Windows Script Component. Provide a name and location for your new file and specify a name for the workspace.
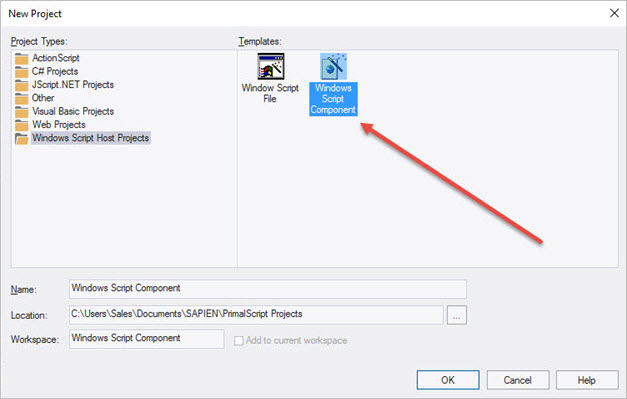
Next, specify the basic properties:
•Name of the script
•Location where the script will be stored
•ProgID which will be used to reference the component
•Scripting language
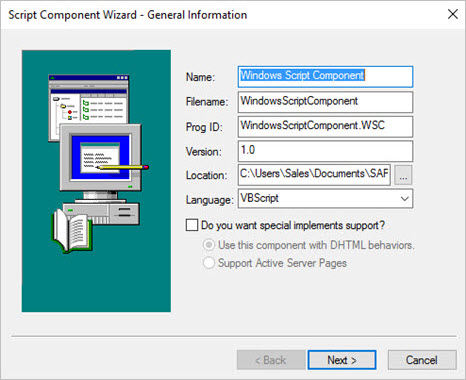
Next, select any objects that will be used within the component. You can click Browse to add objects which aren't on the default list. By referencing the objects that your scripts will use, you can use any constants defined in the objects' type libraries.
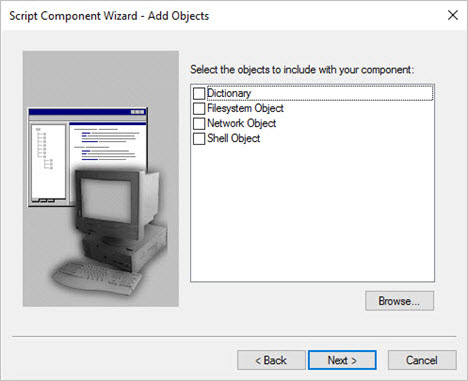
Similarly, you can add various other references in the Add References dialog.
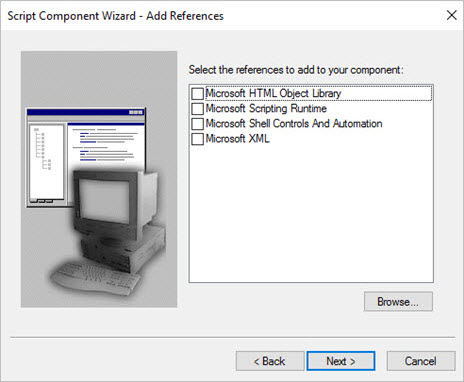
Finally, you can add additional files to the component. These can be automatically copied to the script folder if desired.
After completing the Wizard, your new WSC will be ready. You can begin managing it by using the Workspace Browser.
WSC Workspace
The WSF is part of a special PrimalScript workspace. You can add additional components and their scripts to the workspace. To do so, right-click the top-level workspace item in the Workspace Browser and select Add new component to workspace. The context menu also offers options to add the workspace to source control (or, if it’s already been added, check it in or out).
You can also open the workspace (that is, the WSC file) as a text file. Doing so provides access to the raw XML formatting as well as the script code of the jobs contained in the workspace.
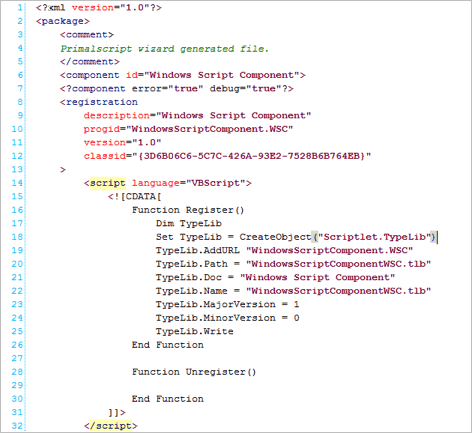
Right-clicking in the editing pane allows you to switch back to the workspace.
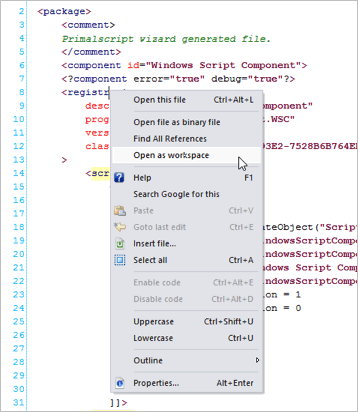
The Workspace Browser provides the key to managing the file. In addition to the actions available by right-clicking the top-level workspace item, you can also right-click a component (the next level of item) or any of the items within a job.
Right-clicking a component (such as “Windows Script Component,” shown here) provides a number of options:
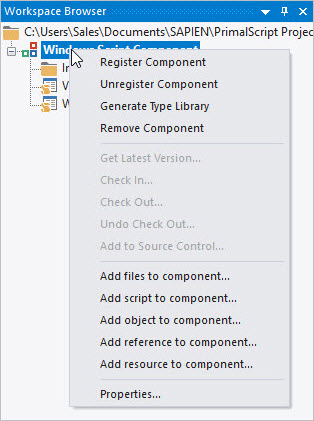
Modifying the component’s properties allows you to change its ProgID, description, and other details.
Right-clicking other objects—such as objects, references, or scripts—allows you to remove or rename them, as appropriate.
Remember, each WSC file, or workspace, can contain multiple components. Each component can contain one or more scripts, files, references, objects, and so forth.
WSC Code
Script code is included within the WSC normally using the PrimalScript code window. PrimalScript handles the XML formatting necessary to enclose the script within its job and the job within the overall WSC.
WSC Properties, Methods, and Events
Just as with regular COM components, a WSC can have members—properties, methods, and events, these are added by right-clicking the Interface item in the Workspace Browser and selecting the appropriate menu item.
When adding a method, you’ll specify its name and any parameters it will accept.
PrimalScript will create the necessary function shell to implement the method. Similarly, creating a property allows you to indicate if it is a read/write property, a read-only property, or a write-only property, and PrimalScript creates the appropriate routines to handle the getting (reading) and setting (writing) of the property.
Note that members can have different external names (the names used when programming with the component from within another script) and internal names (the name the member is known by within its own script).

Using a WSC
Before a WSC can be used, it must be registered, just like a COM DLL.
To register a WSC
•Select Script > Components > Register active component, then click the Register Component button on Script toolbar or right-click the component in the Workspace Browser and select Register Component.
The component can be unregistered in the same way.
 You can also generate a type library (.tlb file) for the component which allows features like PrimalSense to function for the component’s members.
You can also generate a type library (.tlb file) for the component which allows features like PrimalSense to function for the component’s members.
See also: